The Master Document View
A book is ideally suited to the master document feature. Each chapter can be a subdocument, and the elements common to the entire book can be contained in the master document itself.
A master document contains two things: normal document stuff-text and graphics, tables and text boxes, and so on-and links to other documents. Those links can be used to pull in the information from the documents to which the master documented is linked.
The Master Document buttons (you can see these buttons in Outline view that you can choose in View -> Outline):

![]() Master Document View - Switches between Master Document and Outline
views, and expands and contracts the toolbar.
Master Document View - Switches between Master Document and Outline
views, and expands and contracts the toolbar.
![]() Expand/Collapse Subdocument - Expands the master document, by pulling in data from
the subdocuments, or collapses the document, by removing the information and displaying the links to the
subdocuments.
Expand/Collapse Subdocument - Expands the master document, by pulling in data from
the subdocuments, or collapses the document, by removing the information and displaying the links to the
subdocuments.
![]() Create Subdocument - Turns selected headings and text into subdocuments,
automatically saving a new document and creating a link from the master document to the subdocument.
Create Subdocument - Turns selected headings and text into subdocuments,
automatically saving a new document and creating a link from the master document to the subdocument.
![]() Remove Subdocument - Pulls the data from the subdocument into the master document and
breaks the link to the subdocument - but it doesn't actually delete the subdocument file.
Remove Subdocument - Pulls the data from the subdocument into the master document and
breaks the link to the subdocument - but it doesn't actually delete the subdocument file.
![]() Insert Subdocument - Enables you to create a link to use an existing file as a
subdocument.
Insert Subdocument - Enables you to create a link to use an existing file as a
subdocument.
![]() Merge Subdocument - Combines multiple subdocuments into one subdocument.
Merge Subdocument - Combines multiple subdocuments into one subdocument.
![]() Split Subdocument - Divides one subdocument into two subdocuments.
Split Subdocument - Divides one subdocument into two subdocuments.
![]() Lock Document - Toggles the entire document or selected subdocuments to a locked or
an unlocked state. Note that this provides only cursory protection, however. Any user can unlock the
subdocument simply by choosing the Lock Document button again.
Lock Document - Toggles the entire document or selected subdocuments to a locked or
an unlocked state. Note that this provides only cursory protection, however. Any user can unlock the
subdocument simply by choosing the Lock Document button again.
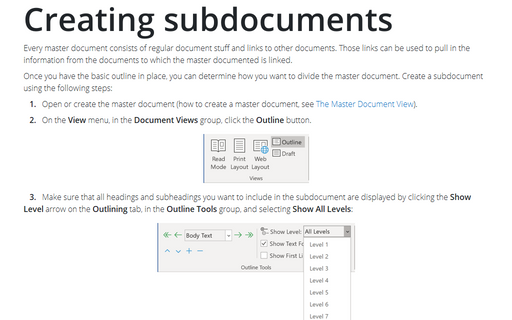
There are three main methods of building a Master Document:
- Begin a new document in Master Document view. Create an outline for your master document, and then use those headings to break the outline into separate subdocuments.
- Break an existing document into subdocuments.
- Combine existing documents into a master document by inserting them as subdocuments. Any existing Word document can be treated as a subdocument.
Starting with an Existing Document
1. Open the document that you want to use as your master document.
2. Change to Outline view by choosing View -> Outline.
3. Assign a heading style to each heading (for example, use Heading 1 for the title and Heading 2 for each subdocument). To do this, use the buttons on the Outlining toolbar:
- Click Promote
 (or Alt+Shift+left arrow) to increase the heading level.
(or Alt+Shift+left arrow) to increase the heading level. - Click Demote
 (or Alt+Shift+right arrow) to decrease the heading level.
(or Alt+Shift+right arrow) to decrease the heading level.
4. As necessary, for any content that is not a heading, select the
content and click Demote to Body Text ![]() .
.
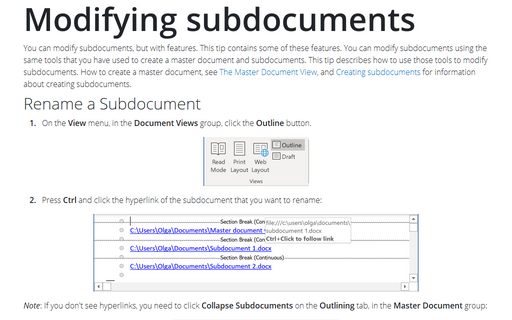
How to create subdocuments from existing document or how to insert subdocuments to the master document, see Creating subdocuments and Importing data for subdocuments.
How to rename subdocuments or split subdocuments, see Modifying subdocuments.
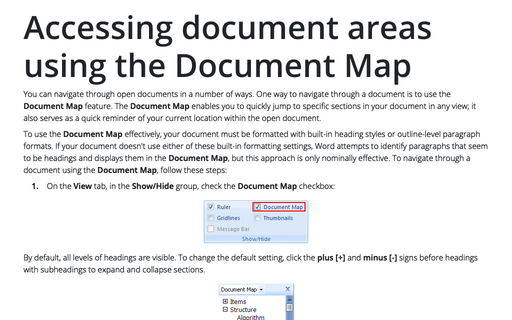
For easy navigation, keep the following keystrokes in mind:
Alt+Shift+Left/Right arrow - Demote or promote the current paragraph and all collapsed subheadings.
Alt+Shift+Up/Down arrow - Swap the current paragraph with previous/next paragraph, moving all collapsed subheadings with it.
Alt+Shift+1 through 9 - Display levels 1 through 9 (for example, Alt+Shift+3 displays levels 1 through 3, Alt+Shift+6 displays levels 1 through 6, and so on).