Working with Microsoft Equation
To insert an equation in your document, on the Insert tab, in the Symbols group, click the arrow next to Equations:
You can use the vertical scroll bar in the Gallery to display additional equations (how to add an equation into the Gallery, see How to add your own equation to the Equation gallery). If you see what you want, click it to insert it at the current insertion point in the document. If you insert it into an otherwise empty paragraph, the equation defaults to appearing in Display mode. If the equation is on the same line as text, it appears in Inline mode:

To write your own equation, do one of the following:
- On the Insert tab, in the Symbols group, click the arrow next to Equations, and then click Insert New Equation,
- on the Insert tab, in the Symbols group, click the Equation button,
- or simply press Alt+=.
Word 2013 opens the Equation Tools Design ribbon:

Word 2013 provides two ways to present equations: Professional and Linear:

By default uses the professional present, but if you ever need linear, simply select the equation(s) you want to change, and click the appropriate tool near the left end of the Equation Tools Design tab:

Equation Tools Design tab contains dozens of equation templates. Within each button on the toolbar, there are several tools available. Simply click on a button to see the tools contained in each. How to create an equation step-by step, see:
- Normal or Gaussian distribution in the tip How
to insert an equation with fractions, square roots and exponents:
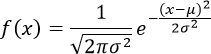
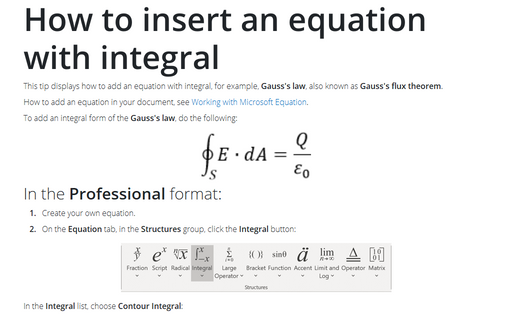
- Gauss's law, also known as Gauss's flux theorem in tip How to insert an equation
with integral:
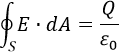
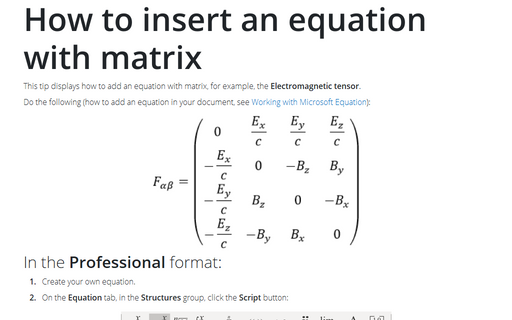
- Electromagnetic tensor in the tip How to insert an equation with
matrix:
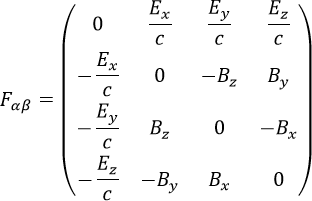
For more details about equations see Setting font size and styles in an equation and Adjusting spacing and alignment in an equation.